
NFTexplained.info is a team of long term crypto investors who are well versed in the blockchain space. In this article our team will provide some insight as to what web 3.0 is as we have received numerous questions and see many misconceptions.
Before we begin, it is important to note that there is no single, universally accepted definition of web 3.0 and that it is currently in the nascent stages but exciting developments are being built every day. Let’s dive in and take a look at what has already taken place!
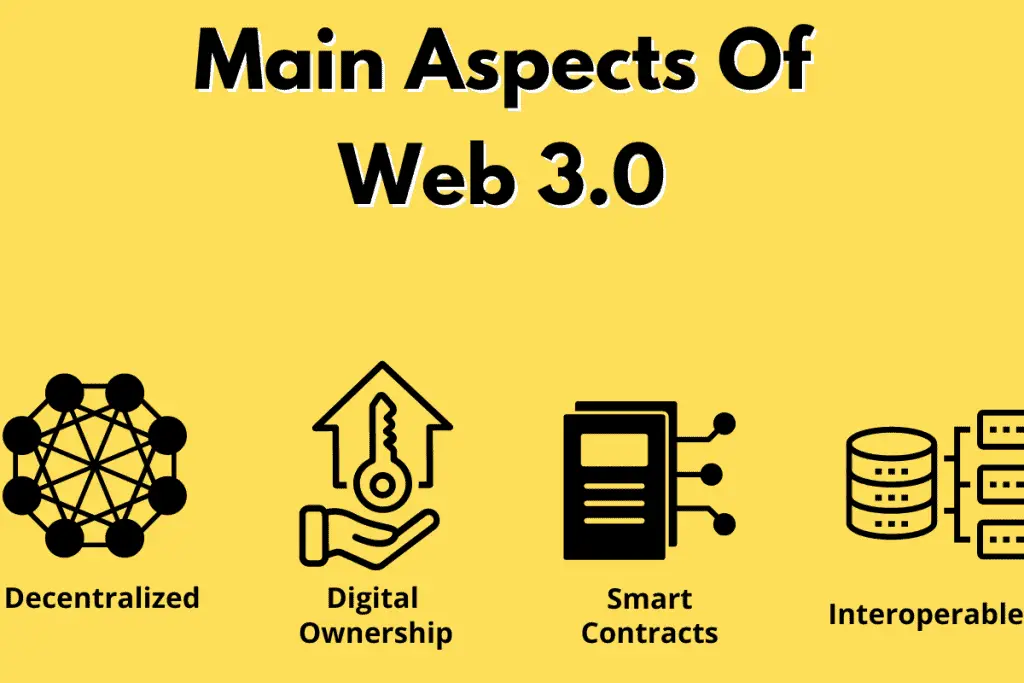
Web 3.0 is the evolution of the World Wide Web; one that is primarily decentralized and enables users to own their assets. Web 3.0 is thought to not be fundamentally owned by a few companies (unlike Web 2.0) but rather decentralized and involving blockchain technology like NFTs.
This may seem far fetched and challenging to comprehend immediately, so allow our team to break down what web 3.0 is component by component.
It is widely agreed upon that we are in the second version of the world wide web and that we are going into the third (aka web 3.0). In the simplest form, web 1.0 allowed users to read. Web 2.0 is what many consider the current stage of the world wide wide web to be in; web 2.0 allows us to interact via reading but also writing or essentially creating content. Web 2.0 is dominated by a small handful of large tech giants – in the English speaking world, Google, Facebook and Twitter are examples.
Web 3.0 is thought to allow users to have ownership of anything digital via NFTs. Web 3.0 will likely not involve large centralized companies but rather be built atop the blockchain, meaning it will be decentralized (involving a form of distributed consensus) and autonomous.
Many think DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations) where users can make proposals and vote will be the primary governing force. Let’s break this down further.
Web 3.0 being decentralized means that the network in which the web will be hosted is spread across computers from all over the world and not a centralized party like Google, Meta, and Amazon (in particular, Amazon Web Services). Since there is no central party controlling web 3.0, users will govern the platform.
Web 3.0 allowing ownership will be done via NFTs or non-fungible tokens. NFTs work by minting or uploading something (like a digital asset) to the blockchain where all users will be able to see proof of ownership. Web 3.0 is thought to be interoperable, meaning users can take their assets and use them in various places across the web; this is a topic we will discuss further in the article.
It is also thought that web 3.0 will involve a digital wallet (like MetaMask) that will allow users to interact with all decentralized applications. Rather than having a username and password for numerous applications, like we currently do in web 2.0 it is widely expected that web 3.0 is thought to only involve a wallet (where assets can be stored).
Web 3.0 is likely to be primarily open source, meaning the source code is available for everyone to see which will likely increase the speed of which a fully functional web 3.0 comes out. This will also allow users to build atop existing versions and add better features.
The currency for which transactions will occur is likely to be cryptocurrencies as that is most compatible across decentralized applications or anything built atop the blockchain.
Not that we have an overall breakdown of web 3.0, let’s take a look at some of the more specific questions our team has received.
Why Is Crypto In Web 3.0?
Crypto – but more specifically blockchain technology – plays a big role in web 3.0 as this version of the World Wide Web is decentralized. Web 3.0 will likely be interoperable, involve smart contracts, and allow for owning digital assets via NFTs.
Web 3.0 will be interoperable in the sense that one single wallet will be connected and that wallet will be able to work across all applications. Currently, we are unable to make different applications work together without coordination.
For example, updating a job status on Facebook does not transfer over to LinkedIn. The same goes for video games – skins or other virtual cosmetics as they can not be used in different games. Web 3.0 is thought to be interoperable across all applications.
Smart contracts will be a driving force in web 3.0 as they allow for the execution of transactions without an intermediary or third party; smart contracts only execute if specific requirements are met.
If you would like to become smart on smart contracts our team will link that article here. Smart contracts will allow users to interact online without the need for a centralized entity to arrange what our team would consider to be a ‘buyer’ and ‘seller’. Smart contracts also remove the fees that a third party would typically take.
What Are Some Examples Of Web 3.0?
One example of web 3.0 is Decentraland, a decentralized virtual world that incorporates many aspects of web 3.0. These aspects include interoperability – some NFTs (digital assets) can be used as in-game characters. Everyone is able to create/monetize their work in game. The game is governed via a DOA and has smart contract features.
Decentraland is often thought to be a web 3.0 company; this is because of the breadth of web 3.0 aspects the virtual world has adopted, including a native cryptocurrency. If you would like to learn more about Decentraland, click here.
We are only able to look at bits and pieces of web 3.0 as it is still in its infancy but we are still able to get a grasp of what it entails by looking at Decentraland.
Digital assets or NFTs – for example, those from the Bored Ape Yacht Club collection – are playable in the Sandbox (which is another virtual world that many would deem comparable to Decentraland). This shows interoperability in its early stages.
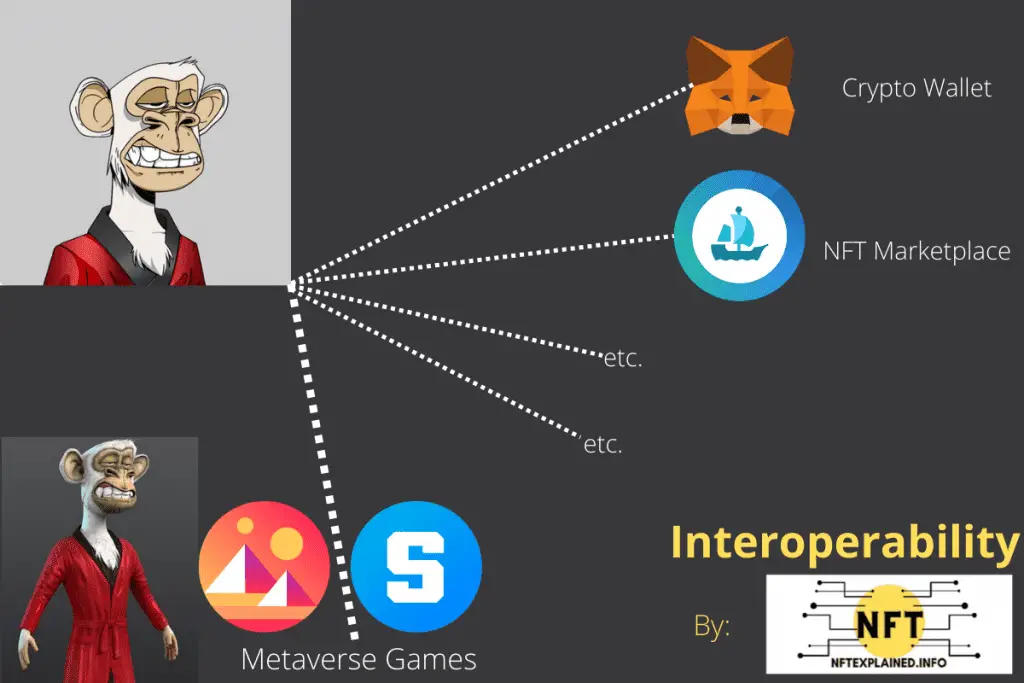
Additionally, because the game is decentralized, users are able to build their own games which can earn them cryptocurrency; this is accomplished by building atop a piece of the games’ land (which is an NFT).
Additionally, the game is primarily governed by a DOA or a decentralized autonomous organization which removes the majority of the governing edicts from a single entity and puts it in the hands of many different users. As a reminder, web 2.0 is frequently criticized as being primarily owned by a few companies whereas web 3.0 is decentralized.
The game also includes the execution of smart contracts for purchasing digital assets if requirements are met. Users are able to have auctions and view digital assets in Decentraland where no third party is involved in the transaction.
All of these aspects – which are related to web 3.0 – are showing what is already happening with blockchain technology in a virtual world and provide concrete examples of what the early stages of web 3.0 include.
As our team mentioned, we are able to see interoperability, NFTs, DOA, smart contracts, and something that is primarily decentralized working cohesively as one.
Okay now that we have an example of what many consider to be a web 3.0 company, let’s take a look at some of the frequently asked questions our team has received; many of which are misconceptions about web 3.0 that you likely have a good grasp on from reading our article.
How Do I Access Web 3.0?
Since web 3.0 is still in the early stages and given there is no universally accepted definition of web 3.0, it is impossible to say how to access it. Since it is widely agreed upon that web 3.0 will involve blockchain tech, accessing web 3.0 will likely be done though a crypto wallet.
As our team previously mentioned it is likely that web 3.0 will be fully interoperable, meaning one wallet will give access to all applications.
What Is The Latest Version Of Web 3.0?
It is impossible to state what the latest version of web 3.0 is as there is no definitive answer as to how close we are to having a fully decentralized web; a fully decentralized web is something widely agreed to be a defining characteristic of web 3.0.
What Is A Web 3.0 Website?
A web 3.0 website is one that is primarily decentralized and involves aspects of blockchain technology or the aspects of web 3.0 that are widely agreed upon. At this point, it is impossible to point directly at a web 3.0 website as there is no globally accepted definition of web 3.0.
Is Web 3.0 A Metaverse?
Web 3.0 is not a metaverse but rather an evolution of the web that includes many aspects that have been newly created from blockchain technology. These aspects include smart contracts, NFTs, being decentralized, interoperability, and more.
If you learned anything from this article, please do our team a favor by following us on Instagram, Twitter & TikTok! As well as subscribe to our YouTube!
Additionally, please consider supporting our team’s content creation through doing business with our partners: Trade stocks & crypto on Webull – get 2 free stocks. Buy a Ledger hardware wallet. U.S. users can get a crypto trading discount on Binance!
