
Having collected exclusive clothing items from various brands in the past, I encountered challenges when purchasing from secondary sellers, such as high-end shoe replicas being misrepresented as genuine products. If these items were digital and stored on the blockchain, I could have easily verified the original creator. This experience highlighted the significance of provenance and its unique role in blockchain technology, particularly with NFTs.
Before delving into the unique opportunities that provenance offers to companies and individuals leveraging the blockchain, let’s first establish a clear definition of provenance.
Provenance can be defined as the history of ownership behind an item starting from the origin. In general, provenances provide documentation about an item like whose hands have touched it which can help verify that an item is authentic.
What is provenance on the blockchain?
Provenance on the blockchain refers to the transparent and traceable record of transactions from wallet addresses. It allows anyone to track the history and movement of funds or NFTs, providing visibility into where a specific wallet has transacted. This ensures transparency and accountability in the blockchain ecosystem.
This is possible because the blockchain utilizes miners (computers that run an algorithm in order to verify transactions); miners are incentivized to do this because they receive a reward and work together by agreeing on a transaction before adding it to the public ledger.
The public ledger is updated each time a new block is added to ensure that all computers have the most up to date information. This means you and I can use blockchain explorers like Etherscan to see what transaction a wallet (e.g. 0x6G8TH54BOX6…) has made.
This provides a higher level of accountability and helps prevent wash trading; additionally, the wallet address is pseudo anonymous as it’s impossible to know who the owner of the wallet is.
A notable person who is heavily involved in identifying rug pulls and wash trading is Twitter user ZachXBT; ZachXBT is an “On-chain sleuth. Rug pull survivor turned 2D detective” who tracks different transfers to help people identify malicious actors in the space.
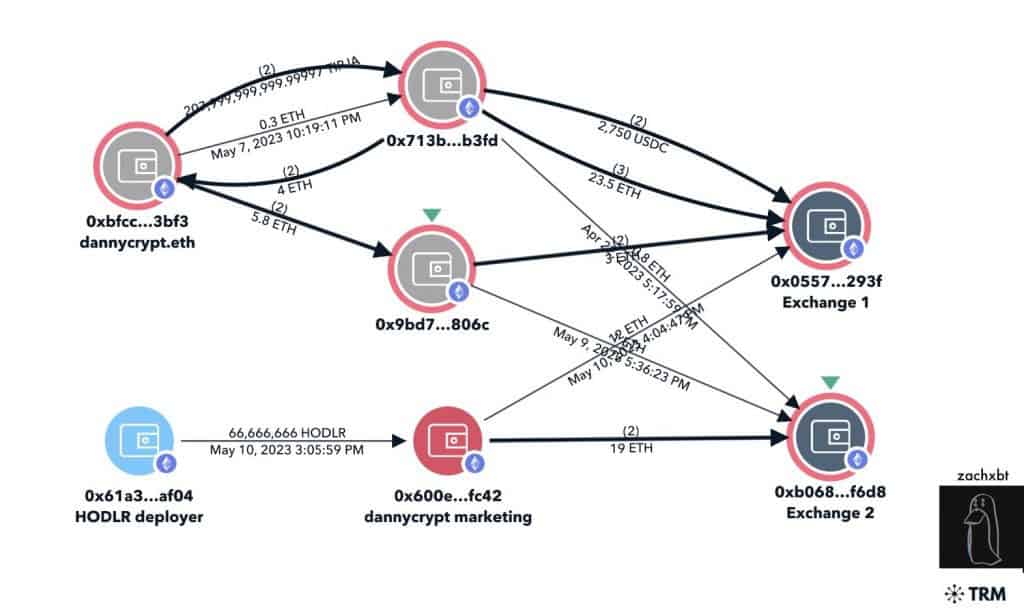
The blockchains’ level of authenticity is furthered by its immutability, meaning nothing can be altered as everything is permanent. The system is irreversible and no changes can be made after an item is tokenized or a transaction has been added to the ledger; this makes the blockchain extremely reliable and challenging to change.
Now, I’ll get back to provenance with regards to NFTs and my previous example of verifying authenticity with real world items in the coming sections.
What Is Provenance In NFTs?
Provenance in NFTs refers to the original creator and transparent ownership history of digital assets; this would include who created and has previously owned an NFT. With blockchain technology, buyers can trust and verify the creator of an item, enhancing transparency.
I will attach a screenshot from OpenSea indicating just how easy it is to see the creator – in this case Beeple – and the previous as well as current owner.
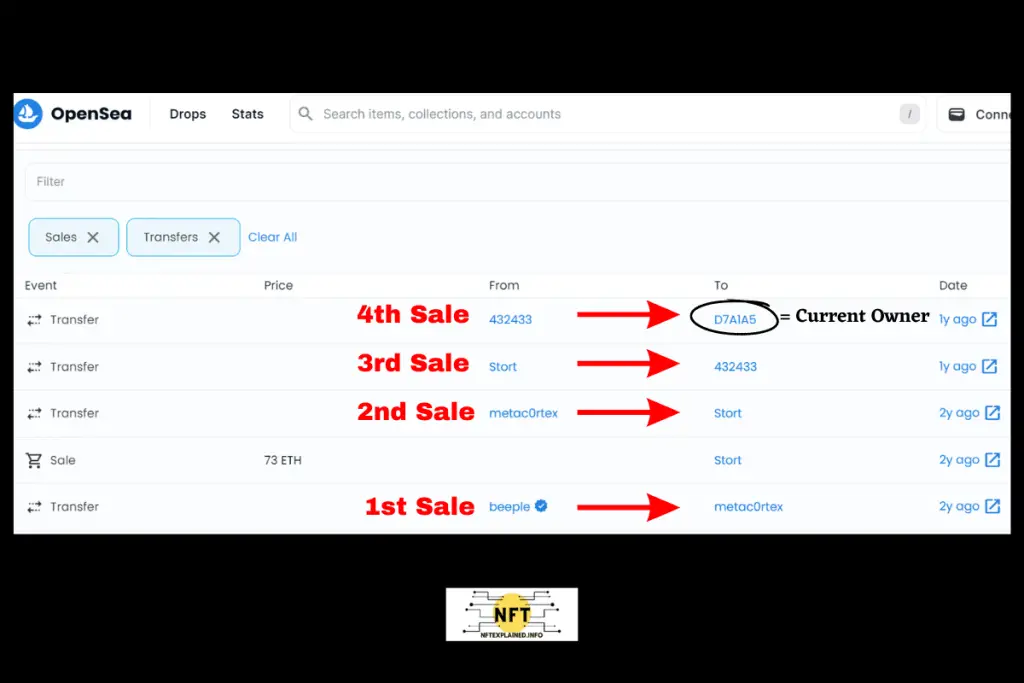
Provenance has shown to impact prices, especially when associated with notable owners. Previous examples demonstrate how ownership by influential individuals can significantly increase the value of an item.
Provenance, enabled by blockchain technology, extends beyond NFTs and artwork. It offers valuable insights across industries. For instance, in agriculture, it empowers consumers to make informed choices about ethically sourced produce.
The blockchain helps identify supply chain issues and their impact on product quality. Provenances’ applications are expanding, benefiting various sectors with transparency and accountability. A notable example of a company infiltrating the supply chain industry is VeChain which has attracted notable partnerships including Walmart China and BMW among other reputable firms.
How Blockchain Provenance Solves Verification Problems With Physical Items
One major problem I faced when collecting exclusive clothing items was the problem of authenticity, especially when purchasing on the secondary market. While digital assets like NFTs on the blockchain are easily traceable, it is more challenging with physical items. One way to do this is through using an NFC (Near Field Communication) in tandem with an NFT.
Physical item authenticity increases with NFC and blockchain tech (i.e. NFTs). By adding NFC chips to items, they can be scanned and represented as NFTs on the blockchain. These NFTs provide valuable information about the item’s origin, ownership history, and authenticity, ensuring its legitimacy.
How NFC works in combination with NFTs is beyond the scope of this article, but if it is something you find interesting, you can read more about that here. Finally, it is worth noting that these chips are continually advancing in sophistication, incorporating tamper-proof features. If someone attempts to remove or scratch off the chip from a piece of art, it will trigger a notification for the user.
In general, I anticipate an increasing prevalence of this issue, particularly in the luxury goods market. The disappointment of purchasing an expensive item, only to discover it is a replica instead of an original from a renowned artist or brand, is a significant concern. Authenticating physical art and goods can be difficult and costly, often requiring an expert familiar with the designer’s work for verification.
In conclusion, provenance plays a vital role in determining the resale value of an item, whether it be physical or digital. The blockchains ability to provide transparency regarding ownership, verifiable authenticity, and additional information such as the item’s creation time is unparalleled in my opinion. Provenance will continue to influence the prices of items, with buyers showing interest in acquiring items with connections to notable individuals.
Furthermore, the increasing popularity of tokenization within the art world indicates a shift in the industry. With more artwork linked to the blockchain, the need for traditional art authenticators may diminish. This shift towards NFTs empowers artists to sell their work online with ease, engaging in direct interactions with consumers in a verifiable manner.
As time progresses, I believe we can expect the widespread adoption of blockchain technology to revolutionize the art market, enhancing trust, accessibility, and efficiency for artists and art enthusiasts alike.
I hope you found this article informative and continue to stay informed with NFT explained. You can find us on YouTube, Instagram, Twitter & TikTok.
If you found value in our content or wish to support our educational mission, you can collaborate with our partners by utilizing these affiliate links: Purchase a Ledger hardware wallet! U.S. users can get a crypto trading discount on Binance!
